
It takes plate in the plant stroma, the inner space in chloroplasts. The Calvin cycle uses the ATP and NADPH produced in chlorophyll to generate carbohydrates. The Calvin cycle is the three-step process that generates sugars for the plant, and is named after Melvin Calvin, the Nobel Prize-winning scientist who discovered it decades ago. (Image credit: Nagendra Yadav via Getty Images) Photosynthesis involves a process called the Calvin cycle to use energy stored from the light-dependent reactions to fix CO2 into sugars needed for plant growth. Light-independent reactions: The Calvin cycle This splitting of water molecules releases oxygen into the atmosphere.
The "electron hole" in the original chlorophyll pigment is filled by taking an electron from water. As it moves through the chain, it generates the energy to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate, a source of chemical energy for cells) and NADPH - both of which are required in the next stage of photosynthesis in the Calvin cycle.
CARBON DIOXIDE FORMULA AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS SERIES
The released electron escapes through a series of protein complexes linked together, known as an electron transport chain. When a photon of light hits the reaction center, a pigment molecule such as chlorophyll releases an electron. The pigments and proteins that convert light energy to chemical energy and begin the process of electron transfer are known as reaction centers. The conversion to chemical energy is accomplished when a chlorophyll pigment expels an electron, which can then move on to an appropriate recipient.

In plants, light energy is transferred to chlorophyll pigments. Ultimately, light energy must be transferred to a pigment-protein complex that can convert it to chemical energy, in the form of electrons.

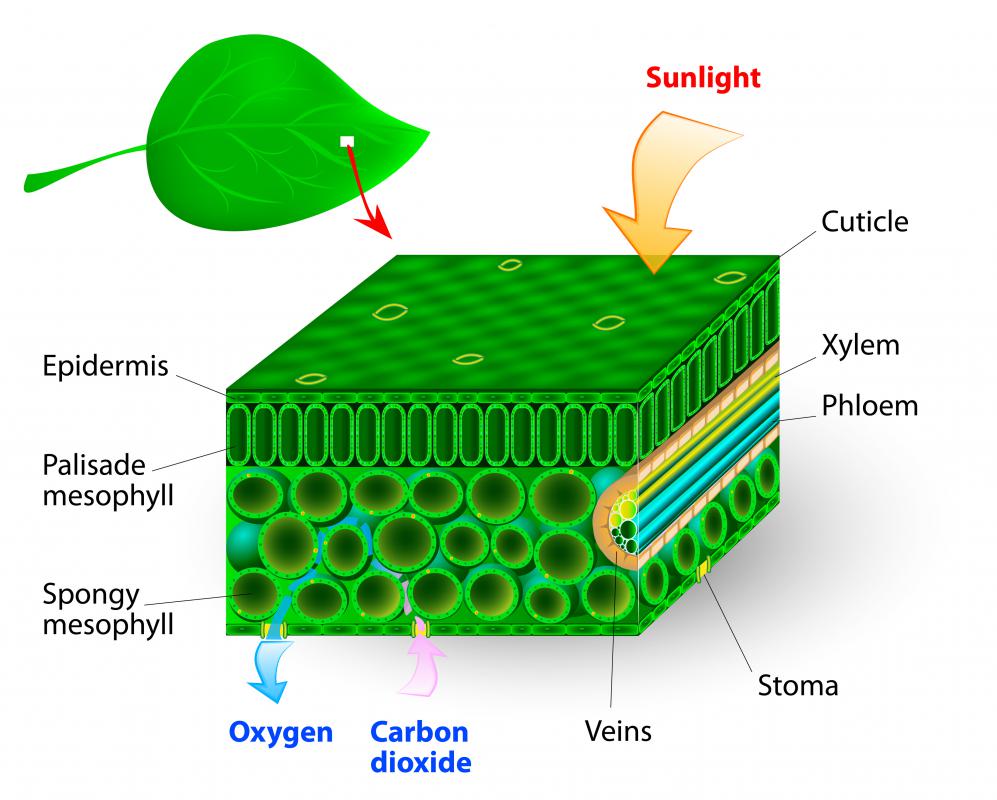
In between the grana is the stroma - a fluid containing enzymes, molecules and ions, where sugar formation takes place. The thylakoids are stacked on top of each other in columns known as grana. Inside chloroplasts are plate-shaped structures called thylakoids that are responsible for harvesting photons of light for photosynthesis, according to the biology terminology website Biology Online. These genes encode proteins that are essential to the organelle and to photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, a type of plastid (an organelle with a membrane) that contains chlorophyll and is primarily found in plant leaves.Ĭhloroplasts are similar to mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of cells, in that they have their own genome, or collection of genes, contained within circular DNA. Plants need energy from sunlight for photosynthesis to occur. Related: What if humans had photosynthetic skin? Where in the plant does photosynthesis take place? While cyanobacteria contain chlorophyll, other bacteria, for example, purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria, contain bacteriochlorophyll to absorb light for anoxygenic photosynthesis, according to " Microbiology for Dummies" (For Dummies, 2019). The situation is a little different for bacteria. These structures effectively capture light energy from the sun, in the form of photons. A large collection of 100 to 5,000 pigment molecules constitutes an "antenna," according to an article by Wim Vermaas, a professor at Arizona State University. Pigment molecules are associated with proteins, which allow them the flexibility to move toward light and toward one another. While carotenoids primarily absorb blue light and reflect yellow, anthocyanins absorb blue-green light and reflect red light, according to Harvard University's The Harvard Forest. Chlorophyll is a large molecule and takes a lot of resources to make as such, it breaks down towards the end of the leaf's life, and most of the pigment's nitrogen (one of the building blocks of chlorophyll) is resorbed back into the plant, When leaves lose their chlorophyll in the fall, other leaf pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins begin to show.

Chlorophyll absorbs red and blue light and reflects green light. Plants contain special pigments that absorb the light energy needed for photosynthesis.Ĭhlorophyll is the primary pigment used for photosynthesis and gives plants their green color, according to science education site Nature Education. How do plants absorb sunlight for photosynthesis? This tradeoff between CO2 gain and water loss is a particular problem for plants growing in hot, dry environments. Stomata close to prevent water loss, but that means the plant can no longer gain CO2 for photosynthesis. When stomata open, they let in CO2 however, while open, the stomata release oxygen and let water vapor escape. Plants absorb CO2 from the surrounding air and release water and oxygen via microscopic pores on their leaves called stomata. (Image credit: Waldo Nell / 500px via Getty Images) Stomata are the gatekeepers of the leaf, allowing gas exchange between the leaf and surrounding air.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
